Caffeine and Weight Loss: Research Confirms 11% Metabolism Boost
Caffeine and Weight Loss: Research Confirms 11% Metabolism Boost
Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed psychoactive substances in the world, largely due to its stimulating effects on the central nervous system. But beyond keeping us awake and alert, caffeine has garnered attention in the health and wellness community for its potential role in weight loss. Recent research highlights that caffeine can boost metabolism by as much as 11%, making it a popular topic for anyone looking to shed extra pounds. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into how caffeine affects metabolism, its effects on weight loss, and practical ways to incorporate it into your diet. Whether you are seeking to augment your weight loss journey or simply curious about how caffeine interacts with your body, this article aims to answer your questions. With a strong focus on clarity and user intent, we will explore everything from the science behind caffeine’s metabolism-boosting properties to tarting safe caffeine consumption practices.
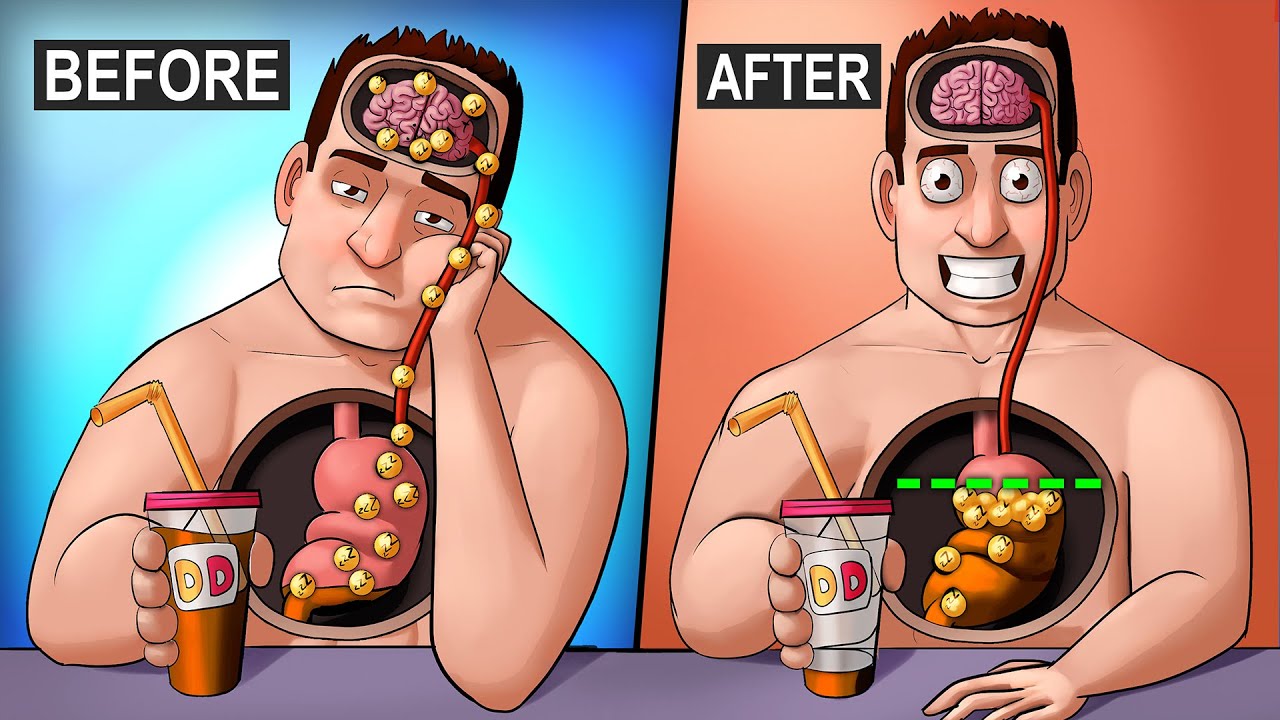
Understanding Caffeine and Its Role in Metabolism
What is Caffeine?
Caffeine is a natural stimulant that primarily affects the brain and central nervous system. Found in coffee, tea, soft drinks, and energy drinks, caffeine is most recognized for its ability to increase alertness and reduce fatigue. However, its benefits extend far beyond just keeping you awake. Studies have shown that caffeine can improve physical performance, enhance mental focus, and even boost metabolism. As we explore how caffeine contributes to weight loss, understanding what it is and how it works is essential.
How Caffeine Affects Metabolism
The metabolic rate refers to the rate at which your body burns calories to maintain basic physiological functions. According to various studies, caffeine can significantly elevate metabolic rate by enhancing thermogenesis— the process by which the body generates heat and energy from digesting food. An increase in metabolic rate means that your body burns more calories, even at rest. Research suggests that consuming caffeine may increase metabolic rates by approximately 11%, which can contribute to greater calorie deficits over time, aiding weight loss efforts.
Comparing Caffeine to Other Dietary Ingredients
When considering weight loss aids, it’s essential to compare caffeine with other commonly touted ingredients, such as green tea extract and various weight loss supplements. While many of these ingredients can offer benefits, caffeine stands out due to its effectiveness and accessibility. Many people already consume caffeine daily through coffee or tea, which makes it an easier choice for incorporation into weight loss plans. Additionally, caffeine can complement other weight loss strategies such as exercise, making it a versatile ally in the fight against excess weight.
The Benefits of Caffeine for Weight Loss
Increased Fat Oxidation
One of the key metabolic processes that caffeine influences is fat oxidation. Fat oxidation involves breaking down fatty acids to generate energy. Studies have shown that caffeine can increase lipolysis— the breakdown of fat stores in the body— effectively shifting the reliance on fat for fuel. Research indicates that caffeine consumption prior to exercise leads to higher rates of fat oxidation, allowing individuals to tap into stored fat during workouts. This increase in fat usage can be especially beneficial for those looking to lose weight.
Enhanced Physical Performance
For individuals engaged in regular exercise, caffeine can act as a performance enhancer. It not only increases energy and endurance but also may lead to more intense workouts. Intense exercise increases the number of calories burned both during and after the workout, contributing to weight loss. By incorporating caffeine before workouts, individuals can maximize their training sessions, leading to improved results in their weight loss journey.
Appetite Suppression
Caffeine may also play a role in appetite regulation. Some studies suggest that caffeine can suppress feelings of hunger, making it easier for individuals to adhere to their dietary plans. For those struggling with cravings or excessive snacking, caffeine can be a viable tool for minimizing calorie intake, leading to more significant weight loss over time.
Safe Caffeine Consumption and Its Sources
How Much Caffeine Should You Consume?
The optimal amount of caffeine for weight loss or performance enhancement varies among individuals, but general guidelines suggest that 300-400 mg of caffeine per day is safe for most adults. This equates to about 3-4 cups of brewed coffee. It’s essential to start with a lower dose if you’re new to caffeine and gradually increase your intake to assess your tolerance level. Understanding personal limits can prevent adverse side effects such as jitteriness, anxiety, or insomnia.
Best Sources of Caffeine
Caffeine can be found in many beverages and foods. The most common sources include:
- Coffee: A leading source of caffeine, with an average of 95 mg per 8 oz cup.
- Tea: Contains varying caffeine levels, generally ranging from 30 to 70 mg per cup.
- Energy Drinks: These can be high in caffeine, ranging from 80 to 400 mg or more, depending on the brand.
- Dark Chocolate: Contains small amounts of caffeine and can also provide health benefits.
- Supplements: Available in pill or powder form, can be convenient but should be used cautiously.
When selecting caffeine sources, consider their additional benefits and overall health implications to ensure a balanced intake.
Potential Side Effects of Excessive Caffeine
While caffeine can be beneficial, excessive consumption can lead to negative side effects including increased heart rate, anxiety, digestive issues, and insomnia. It’s important to monitor how your body reacts and to ensure that caffeine intake does not replace hydration or lead to an unhealthy diet. Listen to your body and adjust your caffeine consumption accordingly to maintain overall health and well-being.
Conclusion: Making Caffeine Work for Weight Loss
Incorporating Caffeine into Your Routine
To effectively use caffeine as a tool for weight loss, consider incorporating it strategically into your daily routine. This might include enjoying a cup of coffee before workouts to enhance performance and fat oxidation or consuming caffeine earlier in the day to minimize the impact on sleep. Pairing caffeine with a balanced diet and regular physical activity can amplify its weight loss benefits. Always remember to stay within recommended limits and listen to your body’s needs.
Long-Term Effects and Sustainability
While caffeine can provide a notable metabolism boost, it’s crucial to view it as a tool and not a weight loss miracle. It should be part of a holistic approach to health that includes nutritious eating, consistent exercise, and lifestyle changes. Sustainable weight loss is achieved through mindful practices that include awareness of how different factors, including caffeine, impact your body. With the right approach, caffeine can complement your efforts toward achieving a healthier weight.
FAQs About Caffeine and Weight Loss
What is the best time to consume caffeine for weight loss?
The best time to consume caffeine for weight loss is typically about 30-60 minutes before workouts. This timing can enhance energy levels and maximize fat oxidation during exercise.
Can caffeine lead to weight gain?
While caffeine can help with weight loss when consumed in moderation, excessive intake may contribute to unhealthy habits, such as relying on high-calorie caffeinated beverages or promoting anxiety and stress that can lead to emotional eating.

Is decaf coffee beneficial for weight loss?
Decaf coffee contains far less caffeine but still has some health benefits, including antioxidants. It can be part of a weight loss plan, but the metabolism-boosting effects will be less pronounced than those seen with regular coffee.
Are caffeine pills effective for weight loss?
Caffeine pills can be effective for weight loss, especially for those looking to control their intake. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements to understand the appropriate dosage and to avoid potential side effects.
How long does caffeine stay in your system?
Caffeine’s effects can last 3 to 5 hours, depending on individual metabolism and tolerance. However, its half-life can range from 3 to 7 hours, meaning that it can stay in your system longer, potentially interfering with sleep if consumed too late in the day.